Why is My Period Brown on the First Day?
Key Facts
- Brown blood on the first day of your period is usually old blood that has taken longer to exit the uterus, causing it to change color as it oxidizes when exposed to oxygen.
- This is completely normal and often your body clearing out leftover blood from the previous cycle.
- Brown discharge can also appear at the beginning or end of your period, especially when the flow is lighter and slower.
- Stress, hormonal changes, or birth control can sometimes cause your period to start off brown instead of bright red.
- If brown bleeding lasts for several days or comes with a foul smell or unusual discomfort, it’s best to check with a gynecologist to rule out infections or other concerns.
Why Does My Blood Become Brown on the First Day of the Period?
Brown menstrual blood is completely normal and happens when blood takes longer to leave the body. First-day period blood may appear brown due to oxidation. When blood leaves the body and is exposed to oxygen, a chemical reaction occurs in the hemoglobin, causing the color to change to brown.
During your period, your uterus sheds blood and tissue. Fresh blood looks red, but if it stays inside longer, oxidation turns it brown.
The brown color can also mean the blood is older and stays in the uterus longer before being expelled. This usually happens when the flow is slow or when the blood takes more time to leave the body.

What Causes Brown Period Blood on the First Day?
Several factors can cause brown period blood on the first day of your menstrual cycle. Here are some of the most common reasons:
1. Oxidation of Blood
First-day period blood may look brown because of oxidation. When blood stays in the body longer and comes into contact with oxygen, it naturally changes color. The longer it is exposed to oxygen, the more likely it is to turn brown.
Many people think brown period blood means it is old, but that’s not true. It’s a natural process of the body.The color of menstrual blood depends on how long it stays in the uterus before coming out.
If the blood stays inside longer, it has more time to mix with oxygen, which can turn it brown.
This usually happens when the flow is slow or takes time to exit. The first few drops at the start of a period are also more likely to look brown because of this process.
2. Slow or Light Period Flow
A slow or light period is a common reason for brown blood. When blood takes longer to leave the uterus, it spends more time in contact with oxygen, which causes it to turn brown.
People with very light periods may see brown blood throughout their cycle. This is more common for those using birth control, which makes periods lighter.
Teenagers who are just starting their periods may also have light bleeding that looks brown. Spotting is normal during this time.
3. Beginning or End of Cycle
Sometimes, brown blood at the start of your period is just leftover blood from your last cycle. Since it stayed in the uterus longer, it changed color due to exposure to oxygen.
It’s also normal to see brown blood at the end of your period. When your flow slows down, blood takes longer to leave the body, giving it more time to turn brown.
4. Implantation Bleeding
If you are sexually active and notice brown spotting instead of your usual period, it could be implantation bleeding, which happens when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining.
Brown period blood can also be a sign of early pregnancy, as light brown spotting is common in the first 12 weeks.
5. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS can cause missed, irregular, or very light periods because of hormonal imbalances. When the flow is light or takes longer to leave the body, the blood may turn brown as it mixes with oxygen.
People with PCOS may also see brown spotting at the start of their period due to irregular ovulation and a delay in shedding the uterine lining.
6. Perimenopause
Perimenopause is the stage before menopause, typically beginning in the late 40s or early 50s. During this time, the body produces less estrogen, leading to shorter or lighter periods.
As menstrual cycles become irregular, changes in flow and color may occur, often causing brown blood at the start or end of a period.
If blood flow slows down significantly, brown period blood may be more noticeable.
7. Lochia (Postpartum Bleeding)
After childbirth, it is normal to have postpartum bleeding, called lochia. It usually lasts about two to three weeks but may continue longer for some women. In the beginning, the blood is reddish-brown, then turns brown or pink, and later becomes pale or white as the bleeding slows down.
Lochia helps the body clear out leftover blood and tissue from the uterus. The amount and color of bleeding gradually decrease over time. Some women may not experience lochia, while others may have irregular periods due to hormonal changes.
If the bleeding is too heavy or lasts longer than expected, it’s important to see a doctor.
8. Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly estrogen and progesterone levels, can affect the timing and flow of your period. If your hormones are imbalanced, the shedding of the uterine lining may occur at a slower rate, causing older blood to be released first.
9. Birth Control Pills
It’s common to have brown period blood, especially when you start a new birth control method or miss a pill. This happens because your body needs time to adjust to the new hormones.
Hormonal birth control contains estrogen, progestin, or both, and it can take a few cycles for your body to get used to the changes. During this time, you may experience brown spotting, also called breakthrough bleeding.
If you’ve just started a new birth control method and see changes in your period, it’s best to check with your doctor for reassurance.
10. Delayed Period
A delayed period can cause brown discharge on the first day. Factors like stress, illness, or weight changes can affect your cycle, causing the uterine lining to break down earlier. As a result, when your period begins, the blood may appear brown.
11. Uterine Fibroids or Polyps
Uterine fibroids and polyps are noncancerous growths that can develop in or on the uterus. Their size and location can affect menstrual flow, sometimes causing irregular bleeding or brown discharge at the start of your period.
Consult a healthcare provider if you notice brown period blood along with any of these fibroid-related symptoms.
Symptoms of fibroids include:
- Menstrual bleeding lasting more than seven days
- Tiredness due to anaemia
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Pain in the pelvis or lower back
- Intense menstrual cramps
12. Endometriosis
Endometriosis happens when tissue like the uterine lining grows outside the uterus. This can cause older blood to become trapped and released slowly, leading to brown period blood.
13. Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and bacterial infections can cause brown discharge mixed with an unusual odor. If you notice other symptoms, such as pelvic pain or unusual vaginal discharge accompanied by brown blood, it’s best to consult the healthcare provider.
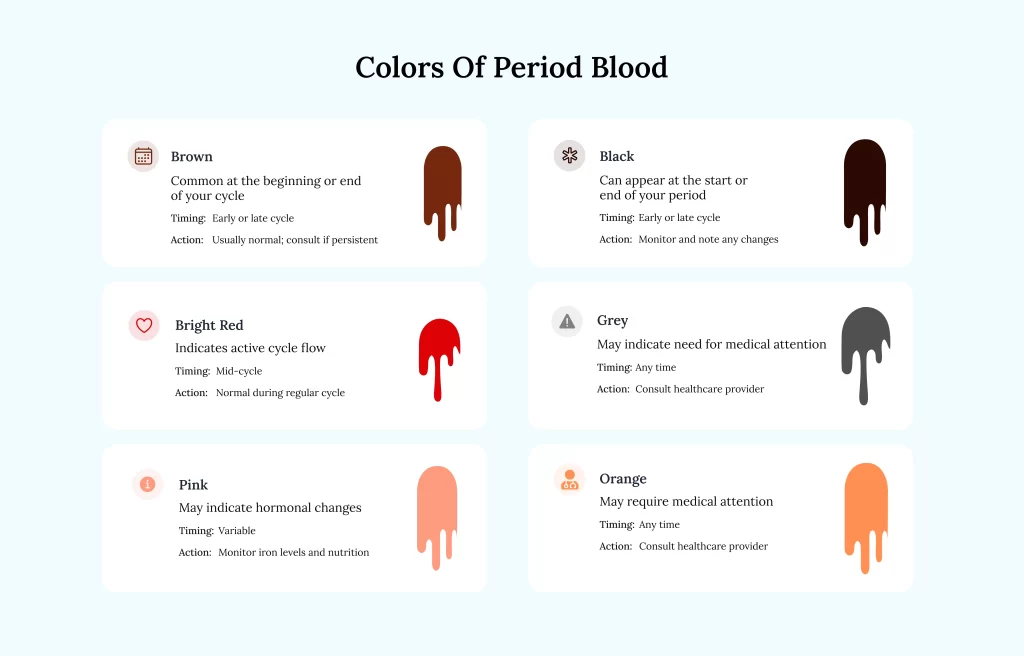
When is Brown Period Blood considered Normal?
Mid-Cycle Spotting – Light brown spotting can happen during ovulation, especially if you just started menstruating, use birth control, or are nearing menopause.
After Childbirth or Abortion – Brown or pinkish discharge is normal after giving birth (postpartum bleeding) or abortion and can last a few weeks.
After Sex – Light brown spotting may happen after sex due to friction or not enough lubrication, which can release old blood.
When Should You Be Concerned?
Brown period blood is usually not a cause for concern, but in some cases, it could indicate an underlying health issue. Consult a doctor if you notice:
- Bad-smelling discharge along with brown period blood
- Severe cramps that don’t improve with pain medication
- Irregular periods with major changes in flow or duration
- Heavy bleeding that fills a pad or tampon within an hour.
- Signs of infection, like fever, itching, or unusual discharge
- Prolonged periods lasting more than seven days, which may indicate hormonal imbalances or fibroids
How to Improve Your Menstrual Health?
If you often notice brown period blood and want to improve your menstrual health, here are some simple and effective tips:
- Eat Nutrient-Rich Foods
Include iron-rich foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and lean proteins in your diet to support hormonal balance and healthy blood flow. - Drink Plenty of Water
Staying hydrated helps your body flush out toxins and promotes a smoother menstrual flow. - Manage Stress
Stress can disrupt your cycle. Try meditation, deep breathing, or yoga to keep your hormones in balance. - Stay Active
Regular exercise improves blood circulation and can help reduce hormonal imbalances that lead to irregular periods. - Monitor Your Cycle
Use a period-tracking app to identify any unusual changes in your cycle and spot patterns that might need medical attention. - See a Gynecologist if Needed
If you frequently experience irregular cycles, brown blood, or other unusual symptoms, consulting a doctor can help you understand and address any underlying health concerns.
Conclusion
Brown period blood on the first day of your cycle is typically a sign of older blood being expelled from the uterus. While it’s generally harmless, consistent changes in menstrual flow, unusual symptoms, or irregular cycles should be discussed with a doctor.
Your menstrual cycle is a reflection of your overall health, and staying informed is key to maintaining your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it normal to have a brown period on the first day?
Yes, it’s normal to see brown blood on the first day. This usually happens when old blood takes longer to leave the body. It’s just your body clearing out leftovers from the last cycle.
Is brown period blood bad?
No, brown blood during your period isn’t bad. It simply means the blood is older and has had time to oxidize. This is a natural part of many healthy menstrual cycles.
Why is my period blood brown on the first day—am I pregnant?
Not usually—brown blood on the first day doesn’t mean you’re pregnant. It often means your period is starting slowly with older blood. If you’re unsure, taking a pregnancy test can help confirm.
Why is my period blood brown the whole time?
If your period stays brown from start to finish, it could mean your flow is light or slow. This lets the blood stay in your uterus longer, which changes its color. It’s not usually a problem unless your cycle has changed a lot.
Brown blood instead of period—what does it mean?
Seeing only brown blood instead of a normal period might mean spotting, hormone changes, or even early pregnancy. It can also happen with stress or birth control. If it happens more than once, it’s good to check with your doctor.
Dark brown discharge for 2 days instead of period—what’s happening?
Dark brown discharge for a couple of days could be old blood coming out late. It might happen if your period is lighter this month or starting differently. If it keeps happening, talk to a doctor to rule out any health issues.